NASA's New Horizons Captures A Day In The Life Of Pluto And Charon, 3 Billion Miles From Earth
NASA's New Horizons spacecraft is more than 3 billion miles from Earth and heading toward Pluto, and while it won't reach the dwarf planet until July 14, one of its cameras was able to observe Pluto and Charon, its largest moon, for a little more than 6 1/2 Earth days, the equivalent of one day on Pluto-Charon.
New Horizons, which left Earth in 2006, began its observation of Charon as it orbited Pluto on Jan. 26 at a distance of 126 miles from the dwarf planet and its satellite. The spacecraft is traveling around 31,000 miles per hour, according to NASA, and over the course of 6.4 days, its Long-Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) captured a full day and moved 5 million miles closer to its target. The time-lapse GIF of New Horizons' images shows the gravitational pull of Charon, which causes Pluto to wobble.
While it may look like two dots to us, the images from New Horizons are helping NASA set up the spacecraft's trajectory. "These images allow the New Horizons' navigators to refine the positions of Pluto and Charon, and they have the additional benefit of allowing the mission scientists to study the variations in brightness of Pluto and Charon as they rotate, providing a preview of what to expect during the close encounter in July," Alan Stern, the New Horizons principal investigator from the Southwest Research Institute, said in a statement.
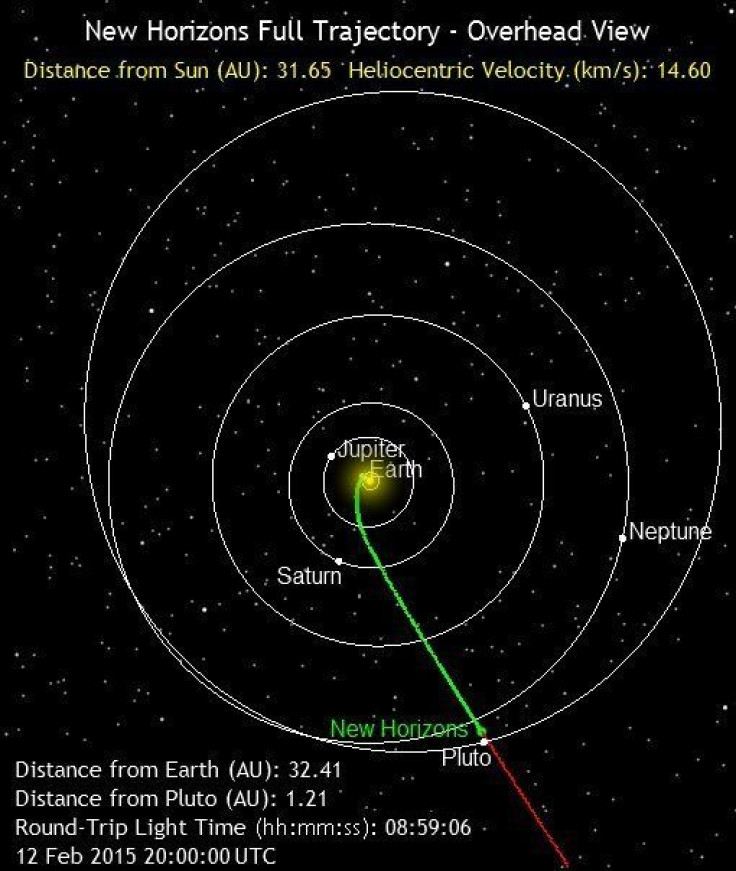
Through its journey, New Horizons has passed each of the planets and captured images of Neptune as well as Jupiter and its moons. As the spacecraft gets closer, expect to get clearer images of Pluto and its moons.
New Horizons is not the only spacecraft targeting a dwarf planet. NASA's Dawn is much closer to Ceres than New Horizons is to Pluto and has been delivering incredible images of the dwarf planet. Dawn most recently took an image of Ceres from 90,000 miles away.
© Copyright IBTimes 2024. All rights reserved.












