Samsung Will Play Fair With Galaxy Benchmarks As Of Android 4.4 KitKat Update
Samsung is notorious for skewing the benchmark results for its popular Galaxy devices in order to make their processors appear much more powerful than they are under normal circumstances. But with the implementation of the Android 4.4 KitKat update, the Korean manufacturer has dismantled the mechanisms that have enabled it to fudge benchmark results in the past.
Last year, Samsung released its Galaxy S4 and Galaxy Note 3 flagships, and several reports accused the manufacturer of skewing benchmarks to make its devices appear to run faster. Samsung has long denied these claims, but recently, Ars Technica discovered code with Samsung’s versions of older Android versions, which was used to maximize CPU output on Galaxy devices when benchmarked. The tech website detailed that the Samsung-specific Android 4.3 Jelly Bean included this code, which made Galaxy devices run all of their CPU cores at maximum speed in the presence of a benchmark application. This would result in benchmark numbers much higher than seen in everyday processing.
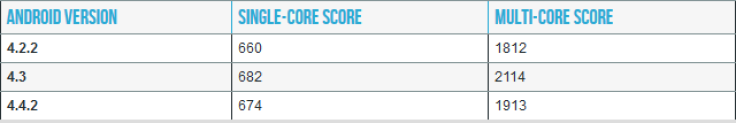
Ars Technica tested an AT&T Galaxy S4 and a Sprint Galaxy Note 3 running Android 4.3 and then running Android 4.4 to see how devices’ CPUs functioned before and after updating. According to the tech website, this benchmark boosting code has been removed from Samsung devices with the Android 4.4 update and Galaxy handsets now report benchmark results according to their processing volume at the time and not according to whether a benchmark is present.
The Samsung Galaxy S4 features a Qualcomm Snapdragon 600 processor, which runs at maximum speeds of 1.9GHz, and the Samsung Galaxy Note 3 features a Qualcomm Snapdragon 800 processor, which runs at maximum speeds of 2.3GHz. These devices have the capability to run at maximum power, but are not required to at all times, in fact most everyday processing for the average user likely does not require maximum processing.
Android 4.3 users should keep in mind that this code does not affect how the system works, only how the system reacts to benchmarks.
Notably, with the benchmark boosting code removed, Galaxy devices running Android 4.4 saw better benchmark results than those running Android 4.2, showing that Android systems have improved processing speed over time.
Currently, Samsung is updating its Galaxy S4 and Galaxy Note 3 handsets worldwide; thus far the Sprint Galaxy Note 3 and Galaxy S4, the U.S. Cellular Galaxy Note 3 and Galaxy S4, the AT&T Galaxy S4, and the T-Mobile Galaxy Note 3 models have begun updating to Android 4.4 in the U.S. Samsung has confirmed that 14 Galaxy devices in the U.S. will update to Android 4.4.
© Copyright IBTimes 2024. All rights reserved.












