Super-Fast Venus Winds Speed Up, Acceleration Baffle Astronomers [PHOTOS]
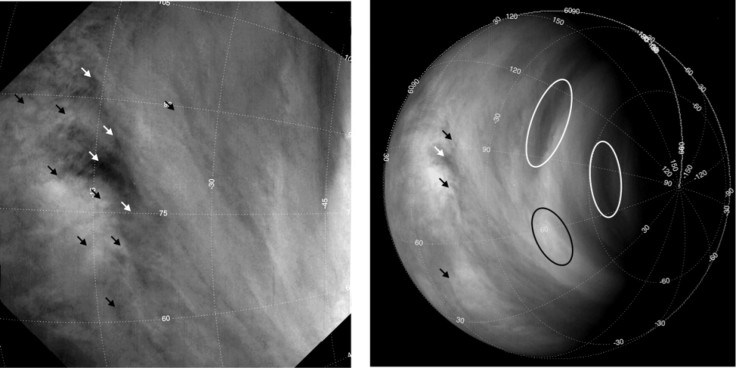
The incredibly fast winds of Venus have been speeding up in the past six years. Astronomers have been studying Venus’ atmosphere but have no explanation as to the cause of the acceleration of Venus’ winds.
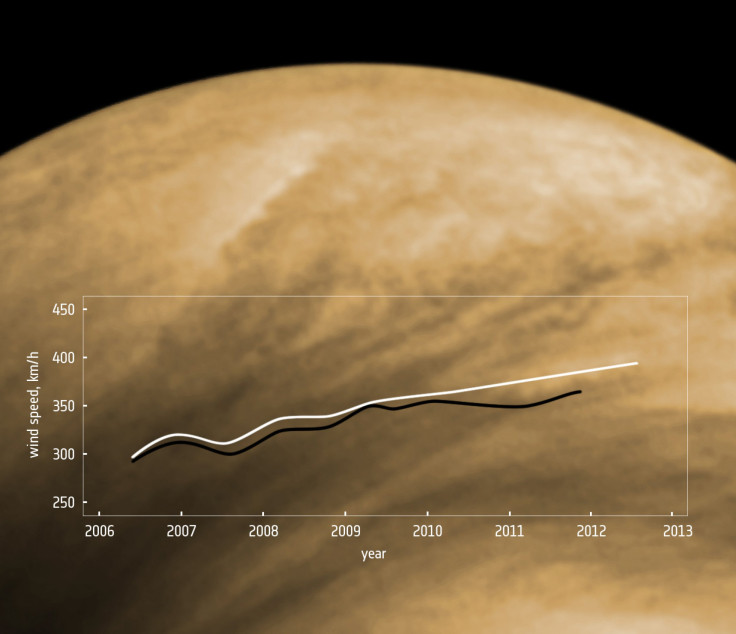
The speed of Venus’ winds is in stark contrast to the planet’s slow rotation. It takes Venus 243 Earth days to make one rotation, according to the European Space Agency, while the atmosphere makes it way round the planet in just four Earth days. To track the speed of the winds, ESA astronomers monitored cloud features for six years via the Venus Express orbiter, which begin studying the planet in 2006. The study will be published in the journal Icarus.
The Venus Express first clocked the winds of Venus at 300 km/h, or approximately 186 miles per hour, but two new studies have shown the winds are getting faster, ESA notes. The winds of Venus are now traveling at 400 km/h (249 mp), and astronomers do not have an explanation for the sudden increase in acceleration.
Over the course of six Earth years, researchers studied 45,000 different cloud features, monitoring how quickly they moved between images, while an additional 350,000 features were tracked by a computer. The Japanese team of astronomers led the computer research, and their study will be published in the Journal of Geophysical Research.
Lead researcher Igor Khatuntsev, of the Space Research Institute in Moscow, said of the discovery, “This is an enormous increase in the already high wind speeds known in the atmosphere. Such a large variation has never before been observed on Venus, and we do not yet understand why this occurred,” the press release notes.
While observing the wind speed change, the two teams of researchers were also able to learn more about the natural atmospheric patterns on Venus. Wind speed and other changes occur based on the time of day, the position of the Sun above the planet’s horizon and the rotation period, ESA notes.
© Copyright IBTimes 2024. All rights reserved.












