Ukraine Crisis Pushes US Inflation To New Four-decade High
Americans paid more for gasoline, food and other essentials last month amid an ongoing wave of record inflation made worse by Russia's invasion of Ukraine, according to government data released Tuesday.
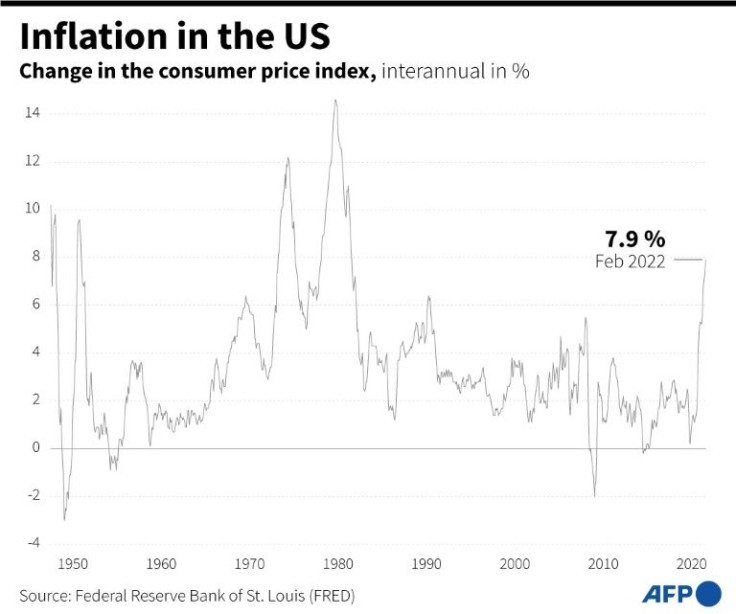
The consumer price index (CPI) climbed 8.5 percent over the 12 months to March, the biggest jump since December 1981 and a sign of the pressure President Joe Biden's administration is under even as it looks for more ways to punish Moscow for the attack on its neighbor.
The inflation surge has dragged Biden's approval lower since it began last year, and the president sought to pin the blame on Russian President Vladimir Putin and the invasion's disruptions to global energy markets.
"Seventy percent of the increase in prices in March came from Putin's price hike in gasoline," Biden argued during a speech in Iowa, though the Labor Department said it accounted for closer to half.

Prices began rising last year as the economy recovered from the Covid-19 pandemic, and while the latest report showed costs hitting new heights for many items, it also contained signs the spike may be leveling off.
Compared to February, prices rose 1.2 percent, in line with analysts' forecasts, but "core" prices, which exclude volatile food and energy sectors, rose 0.3 percent rise, less than expected.
"The Russia-Ukraine war has added further fuel to the blazing rate of inflation via higher energy, food, and commodity prices that are turbo charged by a worsening in supply chain problems," Kathy Bostjancic of Oxford Economics said.
The potency of the ongoing price jumps bolstered the case that the Federal Reserve will take aggressive action at its policy meeting next month, likely raising the key lending rate by half a percentage point as opposed to the quarter-point increase last month.

"With labor shortages pressuring firms to raise wages, we are in the midst of a wage-price inflation cycle that will require extreme action on the part of the Fed to rid the economy of the spreading inflation threat," economist Joel Naroff said.
A collision of factors has fueled the inflation surge, including business' struggles to find enough workers and supplies, the Fed's low interest rate policies, and congressionally approved stimulus measures that drove up demand among American consumers.
In response, the White House has scrambled to offer relief, including by releasing strategic oil supplies to lower prices at the pump and waiving a prohibition on selling a lower-price gasoline blend during the summer months, which Biden promoted during his visit to Iowa.
But the most potent actor in Washington against inflation is the Fed.
Though rate hikes are expected to lower prices in the months to come, central bank Governor Lael Brainard said Tuesday that the fallout from the war in Ukraine "probably skews risks to the upside in inflation."
A new pandemic lockdown in China also "has the potential to lengthen out some of those constraints that we've seen in supply chains," Brainard said in a discussion following the data's release.
The Labor Department data showed Americans are facing real financial pain when they go to purchase must-have items.
Prices for shelter, the category including rents, rose 0.5 percent, while food prices rose one percent overall.
Prices for groceries were up 1.5 percent in the month, and 10 percent over the past year -- the largest such increase since March 1981, according to the data.
However, prices for used cars, which were one of the first items to surge last year, declined 3.8 percent last month, pushing core CPI lower. New car prices rose only 0.2 percent after seeing monthly gains of more than one percent in the latter months of 2021.
But considering how high prices have risen for other categories, Naroff said some on the Fed's policy setting committee may advocate for an even more forceful 0.75 point rate increase next month -- and that would not necessarily bring prices down quickly.
"The ability of any Fed to sharply raise rates to slow extremely high inflation, while not driving the economy into a recession, is limited, especially given factors such as war that are out of its control," he said in a note.
"We are talking about art here, not science, and there is little history of this Fed painting pretty pictures."
© Copyright AFP {{Year}}. All rights reserved.





















