Virus Could Infect More Than 200 Mn In Africa: WHO Modelling

The new coronavirus could kill 150,000 people in Africa in a year unless urgent action is taken, according to a WHO modelling study that says nearly a quarter of a billion people will be infected.
Authors of the research, published Friday in the journal BMJ Global Health, predicted a lower infection rate than in other parts of the world like Europe and the US, with fewer severe cases and deaths.
But while they said many African nations had been swift to adopt containment measures, they warned that health systems could still quickly become overwhelmed.
"Our model points to the scale of the problem for health systems if containment measures fail," said the authors.
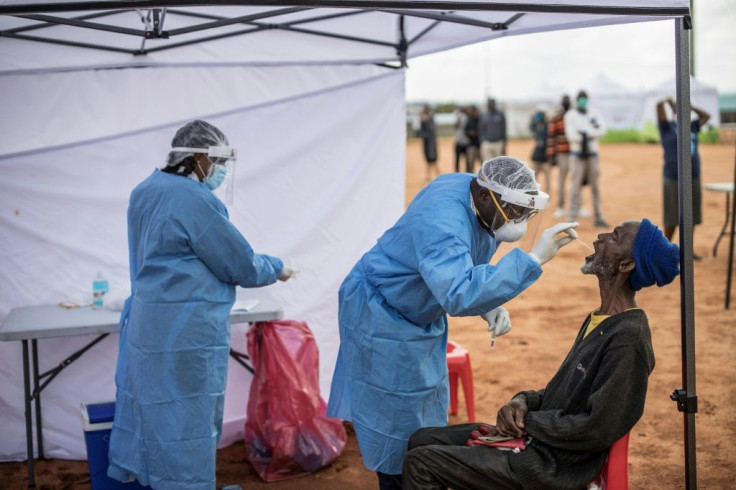
The study comes amid stark warnings that COVID-19 threatens a health emergency in developing nations where fragile health systems are already struggling with an array of other chronic diseases.
Experts at the World Health Organization's Africa office modelled likely rates of exposure to the virus and infection in the 47 countries under its regional remit, which excludes Djibouti, Egypt, Libya, Morocco, Somalia, Sudan and Tunisia.

Some 231 million people, or 22 percent (with a range of 16 to 26 percent) of the one billion people in the region were expected to be infected in the 12 month period -- most of them showing few or no symptoms.
But an estimated 4.6 million people would need to be admitted to hospital, while 140,000 would have severe COVID-19 infection and 89,000 would be critically ill.
That would lead to some 150,000 deaths (between 83,000 and 190,000) the study suggested.
The modelling estimates what would happen for each country over the period of a year from the beginning of widespread and sustained community transmission.

Researchers warned that surging hospital admissions for COVID-19 would divert already limited resources to tackle major health issues in the region, such as HIV, tuberculosis, malaria and malnutrition, worsening the impact of coronavirus.
"The region will have fewer deaths, but occurring more in relatively younger age groups, amongst people previously considered healthy -- due to undiagnosed non-communicable diseases," the report said, adding that these trends were already emerging.
The researchers said they expect the virus would likely circulate within the region for longer than other countries, possibly for several years.
Transmission was estimated to be greatest in small nations, with Mauritius found to have the highest risk of exposure. Of the region's large countries, South Africa, Cameroon and Algeria were also in the top ten for exposure risk.
The authors calculated this risk by looking at each country's "gathering factor" (including family size and population density), people's likely ease of movement, sanitation and hygiene practices.
They also included weather. It is not known if warmer temperatures slow down the spread of COVID-19, though some research has suggested it has that effect on other coronaviruses.
Researchers factored in each country's measures to control the spread of the virus, including physical distancing.
They also looked at health risk factors -- proportion of the population over 65, HIV prevalence (as a proxy for chronic communicable conditions) and diabetes (as a proxy for non-communicable chronic illness).
They called for countries to rapidly boost healthcare capacity, particularly in primary hospitals.
This month the United Nations said the number of deaths from AIDS-related illnesses in sub-Saharan Africa could double if the provision of healthcare to HIV sufferers is disrupted during the coronavirus crisis.
© Copyright AFP {{Year}}. All rights reserved.





















