FDA Warning on Fake Cancer Drug Avastin: How to Tell Counterfeit From Real
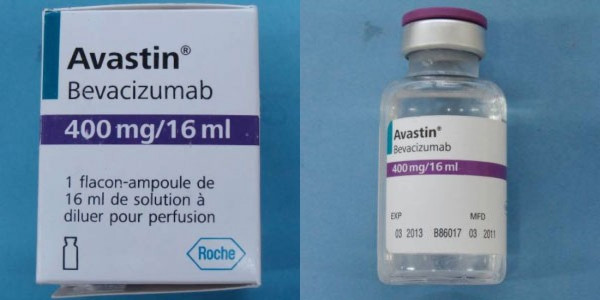
Roche and Genentech, the makers of Avastin, a cancer drug, are warning doctors and patients that a counterfeit version of their drug labeled Avastin (bevacizumab) is circulating the United States. The real drug is marketed by Genentech, a member company of Roche.
Avastin is a prescription-only medicine that is designed, according to its package insert, to interfere with the tumor blood supply by directly binding to the VEGF protein to prevent interactions with receptors on blood vessel cells. By doing this, the drug stops the growth and spread of the tumor. The drug is administered to patients in clinics, hospitals and doctor's offices.
It's an infused medicine and not something a patient would have in their hands, so it's really health care providers who should be on the lookout, said Genentech spokeswoman Charlotte Arnold.
A press statement on the Genentech website explains that the counterfeit products are not safe nor effective. A chemical analysis of the counterfeit drug discovered that the products do not contain the active ingredients for Avastin. Those who have used counterfeit versions of Avastin in treatment will not have received their necessary and much needed treatment.
We're still analyzing what it is, we know it doesn't contain the active ingredient in Avastin, Arnold explained.
The makers of Avastin are currently working with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), as well as law enforcement in an effort to stop the distribution of the counterfeit drug, as well as find its source.
Avastin, the counterfeit medication, does not come in the same packaging as the authentic FDA-Approved drug. Warning signs that the counterfeit drug may be in your possession include a label with Roche as the manufacturer, as well as display batch numbers that begin with B6010, B6011 or B86017.
Currently the FDA has sent letters to 19 medical practices informing them about the counterfeit drug. These medical practices have purchased unapproved cancer drugs, and the counterfeit Avastin may be among them. The drug is suspected of being supplied from Quality Specialty Products (QSP). QSP, sometimes known as Montana Health Care Solutions, is a foreign supplier, and their drugs are not approved by the FDA.
Doctors who believe that they are in possession of the counterfeit drug are said to contact the FDA's criminal unit or Roche's quality assurance department.
This is not the first time that counterfeiters have threatened the safety of the U.S. medicine supply. In 2011, CBS featured a special on counterfeit drugs on 60 Minutes. CBS warned then that some counterfeit drugs are dangerous, and can contain ingredients like highway paint, floor wax and boric acid.
In 2003 the cholesterol reducing drug Lipitor was found to have a counterfeit product, with almost 200,000 tablets being identified as fake. Proficit, a cancer & AIDS drug that fights fatigue and anemia faced similar counterfeit situations in 2002. The counterfeit drugs were watered down with non-sterile tap water, which posed a threat of infection to patients who were already weak.
© Copyright IBTimes 2025. All rights reserved.






















