Reboot the Brain after a stroke?
Researchers found a way to "reboot" the brain by adding adult stem cells to a "brain in a dish" comprised of rat neurons.
It sounds too good to be true, but has medical technology advanced enough to reboot the brain after a stroke?
Researchers at the University of Florida found a way to reboot the brain by adding adult stem cells to a brain in a dish comprised of rat neurons.
When a stroke occurs, there is a central core of death surrounded by silenced neural networks. What researchers did was wake up the quiet circuits and regenerate the core.
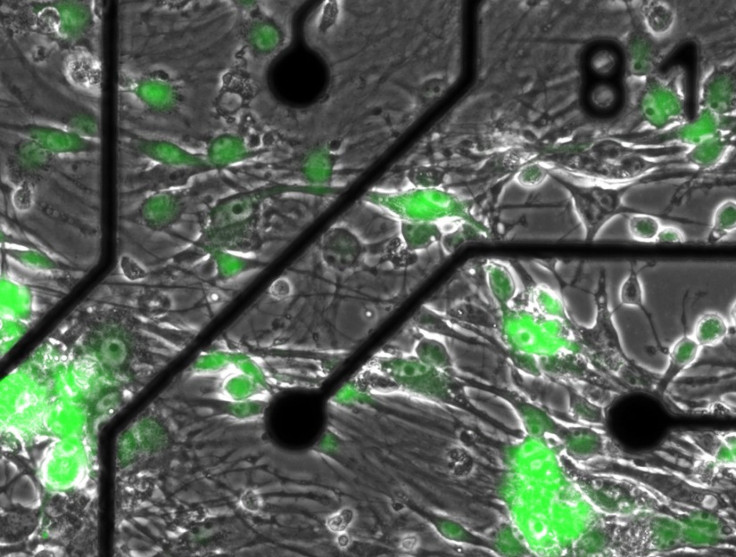
The brain in the dish, also refered to by the scientists as the biologically relevant neural model, is a computer chip with an array of 60 microelectrodes (MEA) that measure the action potential of neurons grown on top. The MEA records the brain cell signals, which are analyzed by scientists.
We take normal neurons, simulate a stroke event, and implant adult stem cells, said Thomas DeMarse, research scientist at the University of Florida. He is working with assistant professor of biomedical engineering Brandi Ormerod and PhD student Crystal Stephens on the transplant model and have recently submitted their findings to the Journal of Neuroscience.
MEA doesnt just tell you the activity of one neuron, it tells you the activity of hundreds at the same time, says DeMarse.
While using MEAs is not new, addding adult stem cells in vitro is.
Scientists put cells from an embryonic rat brain in the dish, and the neurons started talking to one another and gradually worked in unison after the cells showed stable activity patterns.
Then the scientists added the adult stem cells harvest from rats to the network in the dish. The neural progenitors, another word for adult stem cells, were tagged with green fluorescent proteins.
According to Ormerod, the neural progenitors only make brain cells instead of turning into eyeballs or toenails.
After we got the stem cells in, one of the things we wanted to know is, 'Are they functionally integrating into the network?' DeMarse said. One of the first things we saw was a dramatic change in the pattern of activity. There was a super burst of activity.
When an area of the brain is rebuilt, you somehow have to get it to talk to the surrounding areas, Ormerod said.
The adult stem cells might actually do just that - facilitate communication between existing brain cells and new ones.
Through these experiments, scientists are looking for answers such as precisely what happens when stem cells are added and how many cells are needed to restore brain function.
And maybe doctors can one day reboot silenced cells of a brain.
READ: Supreme Commander busted for recruiting for phony Army Unit
© Copyright IBTimes 2024. All rights reserved.



















