What Is The Ring Of Fire? Most Popular Area For Earthquakes, Volcanoes
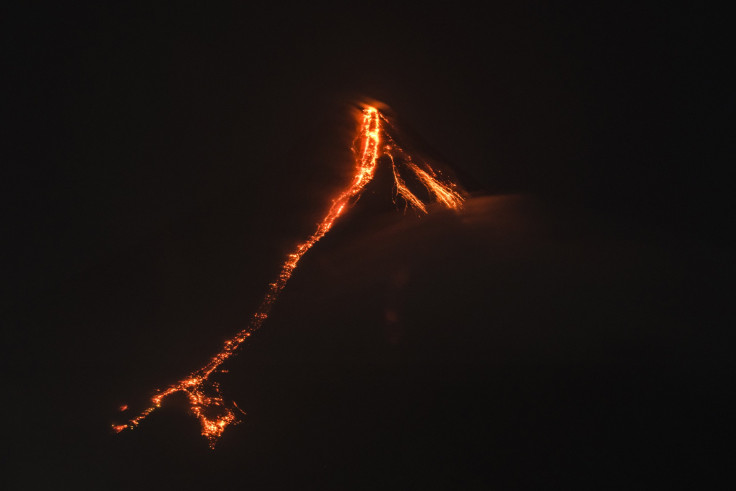

The area along the perimeter of the Pacific Ocean is one of the most active in the world for volcanic activity and earthquakes. The latest volcano's activity to draw the interest of the world was that of the Mayon volcano in the Philippines.
Mayon was erupting earlier this week spewing ash and lava into the air and prompting officials to establish danger zones residents to evacuate the area. Mayon sits in the Ring of Fire along with many other active volcanos.
What is the Ring of Fire?
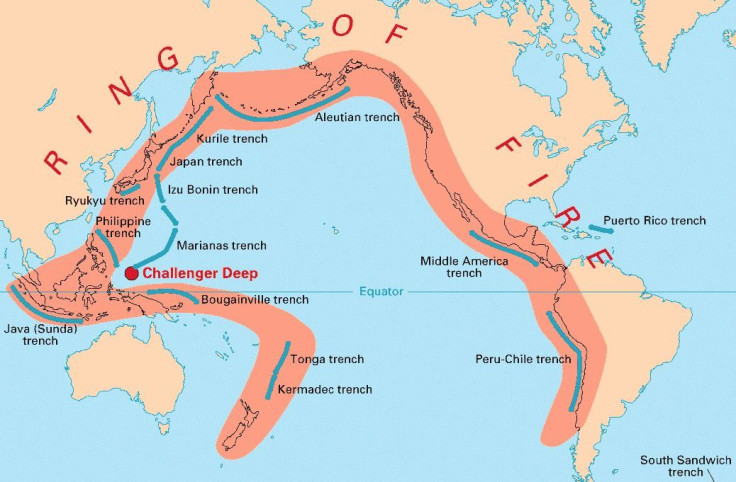
The United States Geological Survey calls the Ring of Fire the area that makes up the margins of the Pacific Ocean where earthquakes and volcanoes "occur abundantly." It's sometimes also called the "circum-Pacific belt," but no matter the name it's known as the area where about 90 percent of the earthquakes on Earth actually happen, said the USGS.
What causes earthquakes?
Earthquakes are caused by a slip on a fault in the Earth. A fault is a part of the Earth where the tectonic plates grind or scrape against one another as they move, according to the USGS. When the plates slip or move suddenly instead of at a graduate pace, they cause a wave of energy to radiate out through the Earth's crust.
How many volcanos are there in the Ring of Fire?
The Ring of Fire contains more than 450 volcanos of the roughly 1,500 in the world over an area that covers almost 25,000 miles. It formed due to plate tectonics where plates come together and one plate ends up under another and the convergence causes melting and forms magma, according to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.
© Copyright IBTimes 2025. All rights reserved.



















