Four-Billion-Year-Old 'Unusual' Battered Volcano Found on Mars (PHOTOS)
The European Space Agency’s (ESA) Mars exploration mission, Mars Express, revealed a large extinct volcano on the Martian surface that is battered and deformed.
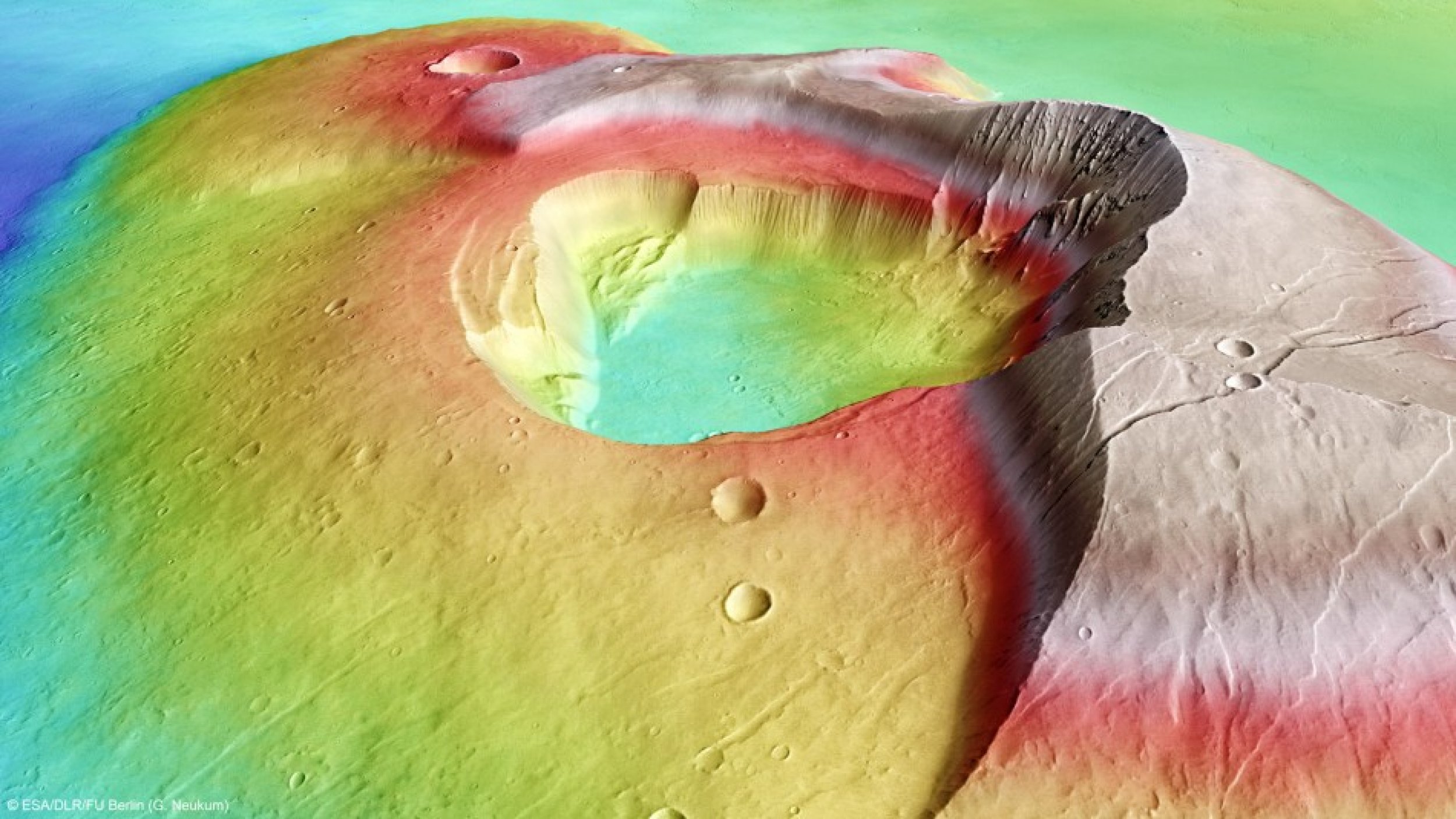
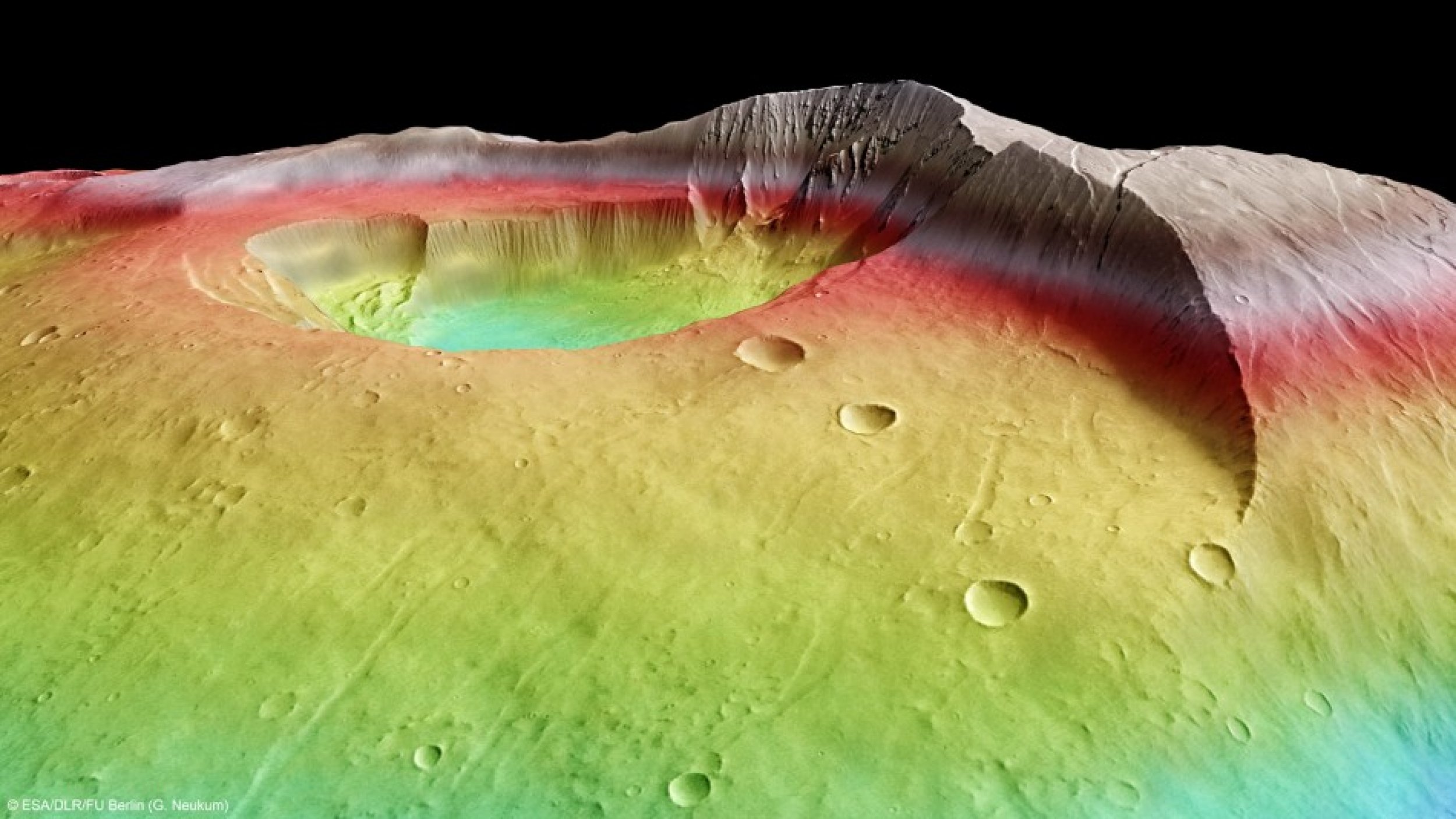
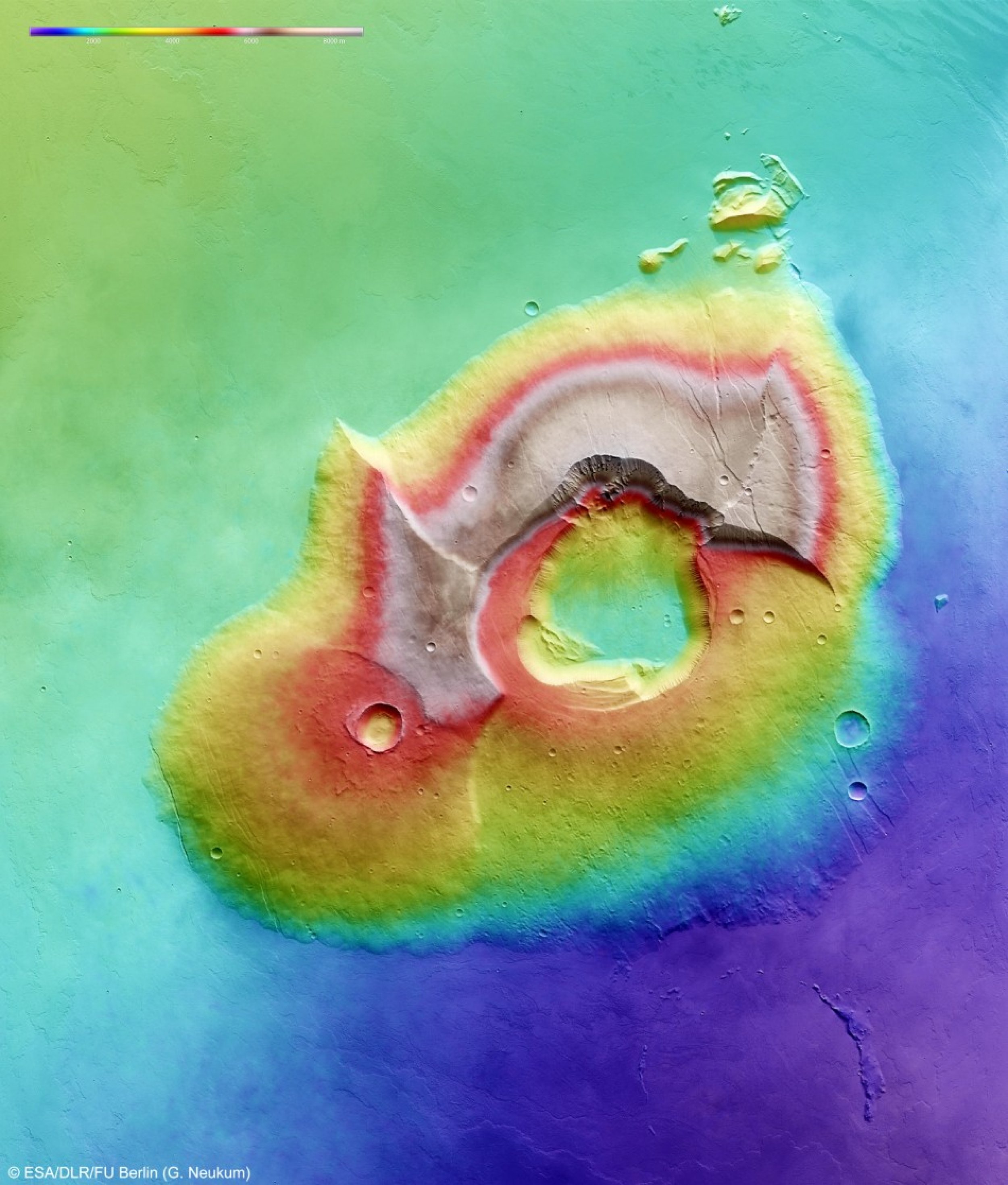
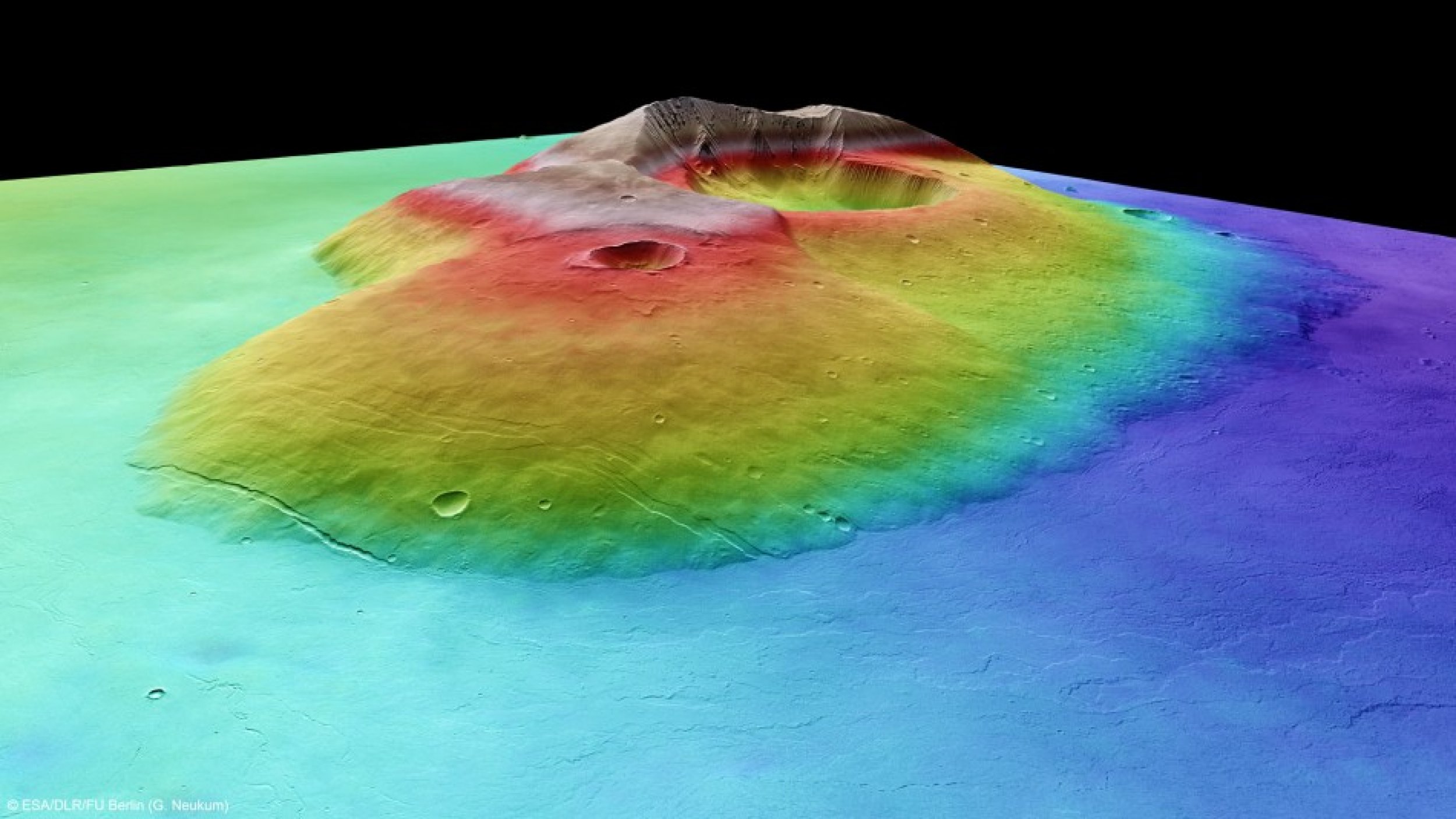
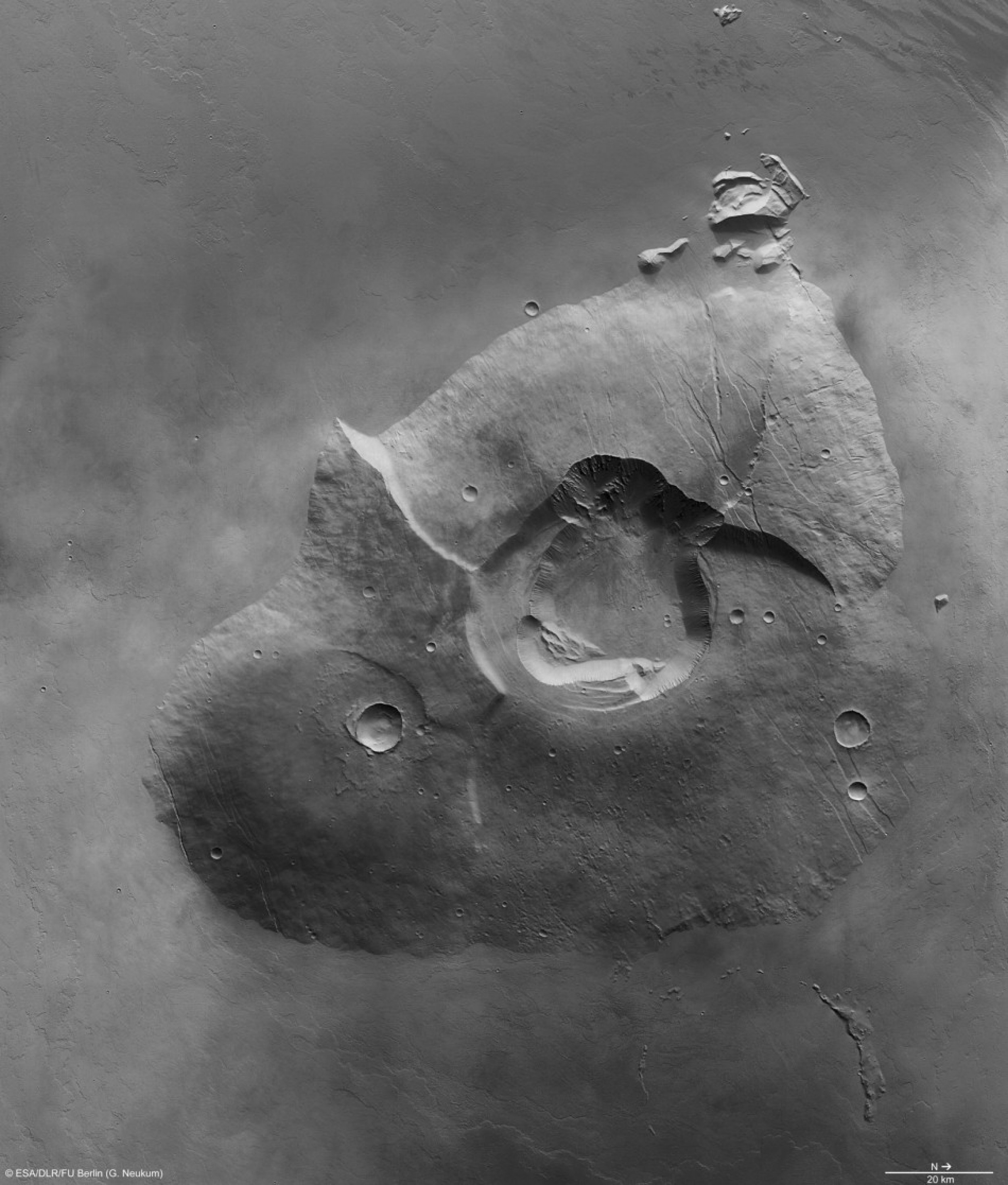
The latest image taken by a high-resolution stereo camera on ESA's Mars Express spacecraft shows the volcano, named Tharsis Tholus, as a giant volcano towering 8 km above the surrounding terrain, ESA officials said Tuesday.
However, just an average-sized volcano for Mars, its “unusual” battered conditioned has baffled scientists.
“At least two large sections have collapsed around its eastern and western flanks during its four-billion-year history and these catastrophes are now visible as scarps up to several kilometres high. The main feature of Tharsis Tholus is, however, the caldera in its centre,” space agency officials stated.
Scientists assume that the eruptions led to empty magma chamber in the volcano making it vulnerable to deformations.
“As the lava ran out onto the surface, the chamber roof was no longer able to support its own weight. So, the volcano collapsed, forming the large caldera,” they explained.
Major space agencies of the world are eyeing landing on the Red Planet. While NASA’s Mars exploration mission intends to search for evidence of water and life on it, Russia's Phobos–Soil is designed to land on Phobos, the larger of Mars' two moons.
Phobos–Soil will “collect samples, and return them to Earth in 2014. It also carries the first Chinese spacecraft to Mars, Yinghuo-1,” added ESA.


© Copyright IBTimes 2025. All rights reserved.





















