Usable Air On Mars: NASA Scientists Want To Remove The Dust For Astronauts
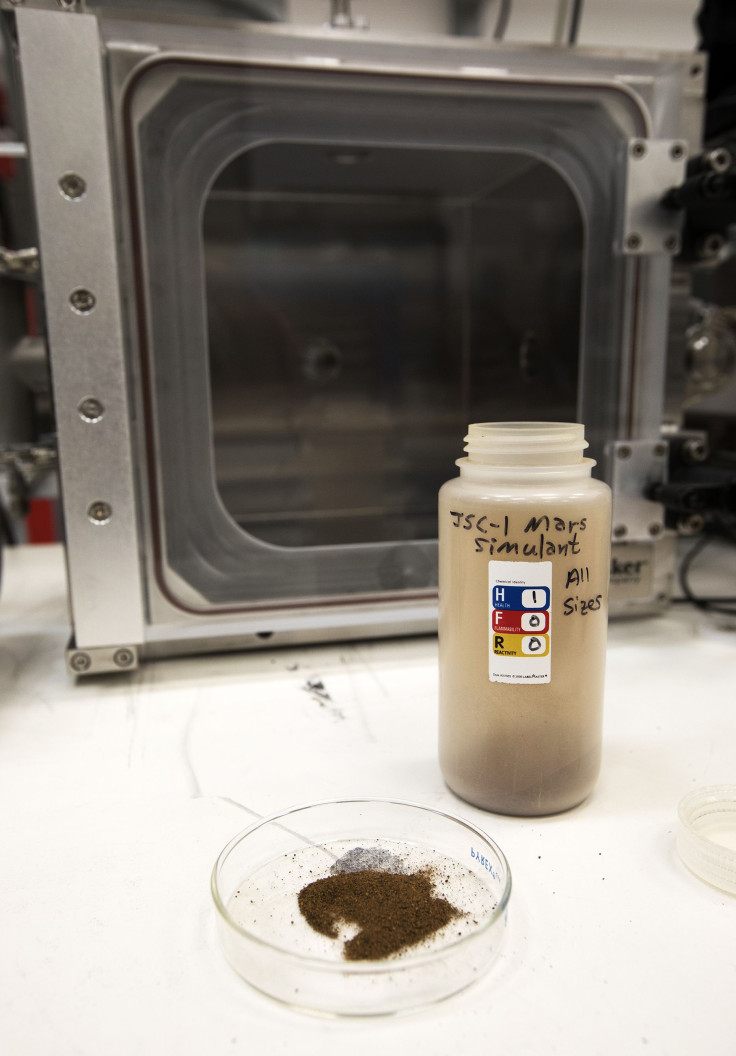

When humans are living and working on Mars, how do we stop that red dust from getting all over us? NASA is working on a way to use static electricity to stop it from choking astronauts and machines.
Scientists have to get the dust out of the equation so it doesn’t damage equipment, NASA’s Kennedy Space Center explained, but there’s also the matter of separating it from the atmosphere that astronauts will be drawing upon to get some of their resources.
Read: 9 Places on Planet Earth That Are A Lot Like Mars
“Commodities such as oxygen water and methane can be obtained from the carbon dioxide-rich Martian atmosphere,” scientist Carlos Calle said in the statement. “Astronauts will need these essentials as they practice in-situ resource utilization.”
In other words, as they use the materials already on Mars to get what they need. The space travelers will have to do that as much as possible since they won’t be able to take everything they could possibly need with them, and the journey home, in the event of an emergency shortage of something, is not very quick.
“Like early European settlers coming to America, planetary pioneers will not be able to take everything they need, so many supplies will need to be gathered and made on site,” NASA said.
A machine called an electrostatic precipitator uses a pair of electrodes to give an electric charge to dust particles that are passing through them so the particles stick to the other side, removing the dust from the air. The electrically filtered air can then be used as a resource.
We use machines like this on Earth, and the NASA scientists are working to make a model that will do the same thing on the Martian surface with its special dust.
Read: NASA’s New Mars Rover Looks Like a Batmobile
“The plan is to send an electrostatic precipitator and other equipment to a landing site to prepare for the arrival of the crew,” researcher Jay Phillips said. “Dust can damage equipment and must be separated from the atmosphere prior to producing the consumables astronauts will require for life support and fuel on Mars.”
The space agency said it’s not as easy as it sounds because Mars has substantially lower air pressure and much more carbon dioxide. It used to have much more air, but the planet has lost about two-thirds of its atmosphere to space since it formed, a change that helped transform it from a warm and water-filled world into the dry and cold place that we know today.
To make the work more exact, the research team has created a dust that will resemble the kind that can be found on Earth’s neighbor. With a little luck, astronauts will be able to use the method to help them survive stays on Mars.
© Copyright IBTimes 2024. All rights reserved.











