Infographic: Huawei Is Ahead Of Others In The Race To Develop 5G
The tension over 5G technology between Chinese telecommunications company Huawei and the United States has reached a variety of low points over the first part of 2019. President Trump most recently called for the U.S.’s allies to not roll out Huawei’s 5G network, citing potential security and data privacy concerns, which allies have not heeded.
5G is the next generation of mobile broadband, which will replace or augment its 4G/LTE predecessor and will set the stage for 6G service. The company that can get ahead in 5G will be able to have more market control over 6G service in the future. The benefits of 5G are faster download and upload speeds, and other measures of network efficiency like latency. These faster download and upload speeds will be essential for processing and moving large amounts of data for services like autonomous vehicles.
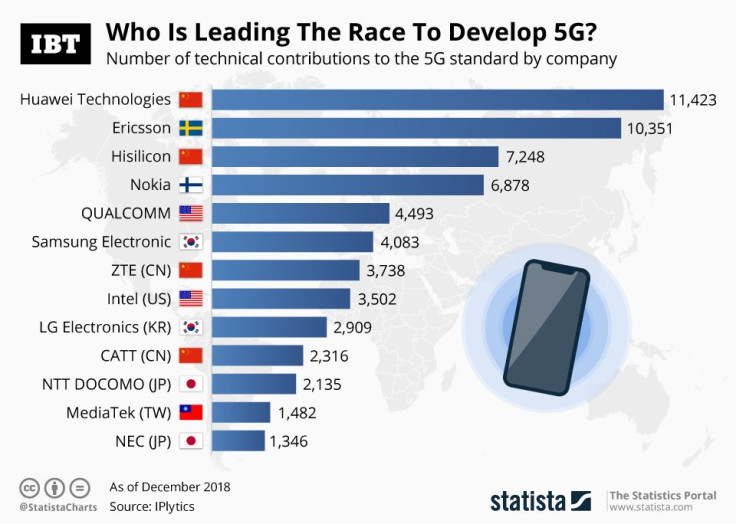
Huawei Technologies, the Chinese tech company, has been aggressively pursuing 5G dominance, adding the most technical contributions to the 5G standard at international conferences where what 5G is and how it will be implemented is outlined. The company has added more than 11,000 technical contributions to the 5G standard. Swedish telecoms company, Ericsson, has added the second most to the standard, adding over 10,000 technical contributions.
© Copyright IBTimes 2025. All rights reserved.





















