Video Captures Possible Meteor Explosion In The US
KEY POINTS
- A fireball event recently occurred over the U.S.
- A video captured the fireball's explosion
- The fireball was most likely caused by a meteor
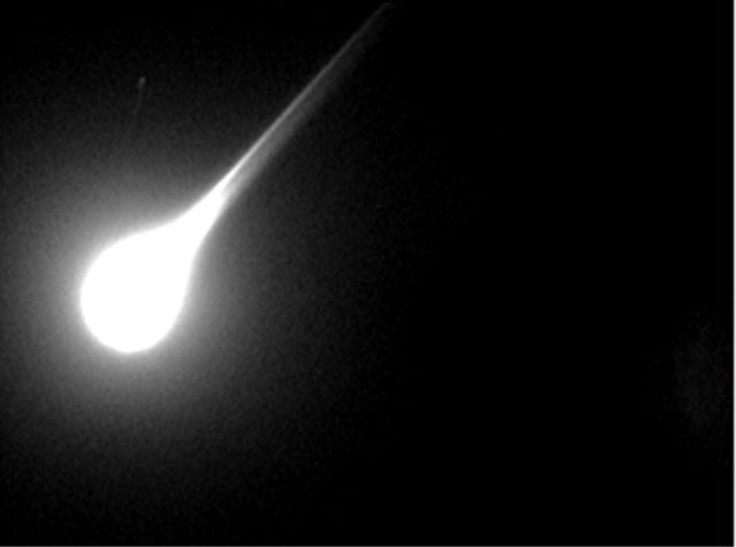
A home’s security cameras were able to capture the moments when a bright fireball streaked across the night sky and produced a powerful mid-air explosion in the U.S. Based on the video and the reports made by other eyewitnesses, the fireball was most likely produced by a meteor that entered Earth’s atmosphere.
The fireball event happened on July 9 at 1:43 a.m. PDT or 4:43 a.m. EDT. It was spotted by eyewitnesses from Washington and Oregon. The eyewitnesses submitted their reports regarding the fireball event to the American Meteor Society (AMS).
As stated in the reports, the fireball appeared in the sky for several seconds. Although its magnitude varied depending on where it was spotted, the eyewitnesses indicated that it appeared brighter than the planet Venus when viewed from Earth.
One of the eyewitnesses, Jason S. from West Salem, Oregon, posted a video of the incident that was captured by his home’s security cameras. The minute-long clip showed the bright flashes produced by the fireball as it flew across the sky.
Aside from the flashes, loud sounds can also be heard in the video. The sounds, which Jason S. likened to gunshots, might have been produced by the fireball’s explosion.
Other eyewitnesses also stated in their reports that they heard loud booming sounds after seeing a bright flash in the sky. Some of them also noted that the fireball fragmented as it flew towards the ground.
Based on the video and the reports submitted by the eyewitnesses, it is possible that the fireball was caused by a meteor that hit Earth and exploded in the air as it entered the atmosphere.
According to the AMS, bolides occur when a meteor or asteroid hits Earth and produces a bright flash in the sky. The flash is produced by the space rock’s explosion as it gets subjected to the intense friction and pressure in Earth’s atmosphere.
“A fireball is another term for a very bright meteor, generally brighter than magnitude -4, which is about the same magnitude of the planet Venus in the morning or evening sky,” the AMS explained. “A bolide is a special type of fireball which explodes in a bright terminal flash at its end, often with visible fragmentation.”
© Copyright IBTimes 2025. All rights reserved.





















