NASA Satellite Image Captures Effect Of COVID-19 Lockdown From Space
KEY POINTS
- Satellite images show the effect of the COVID-19 lockdown in China
- NASA's orbiter detected a sudden drop in NO2 concentrations in China
- China's improving air quality was caused by travel restrictions and lockdowns
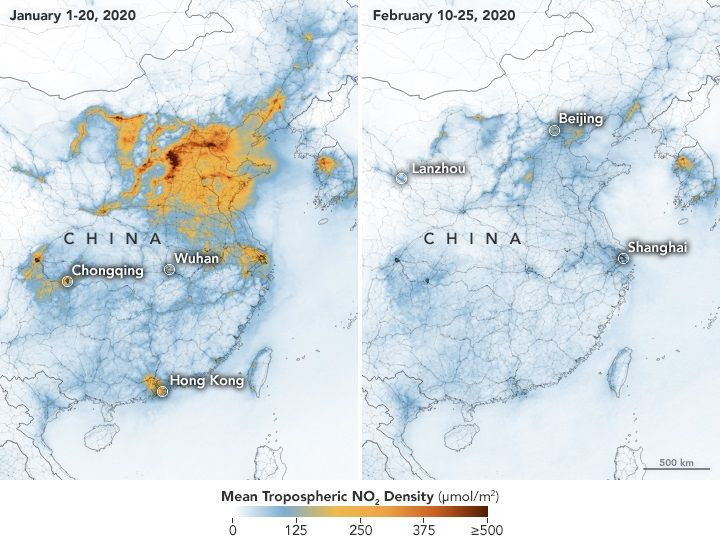
A satellite image captured by one of NASA’s orbiters illustrates the drastic effect of the COVID-19 lockdown on China. The image shows how the travel bans and other local restrictions imposed on China due to the outbreak have affected the air quality in the country.
China currently holds the most number of coronavirus confirmed cases in the world. As a result, local and national governments all over the country have imposed various travel restrictions to prevent the spread of the various. Many companies also ceased their operations due to the health issue.
Although the effects of the lockdowns are very visible from the ground, NASA noted that they could also be spotted from space. According to the agency, its Earth Orbiter, which monitors the planet’s air quality from low-air orbit, was able to capture an image from space that illustrates the effect of the coronavirus lockdown on China.
As noted by NASA, Earth Orbiter’s instruments detected a sudden drop in the concentration of nitrogen dioxide (NO2) in China. This is a toxic substance that is usually emitted by power plants, vehicles and other machines and equipment that burn fossil fuels for energy.
The images captured by the Earth Orbiter clearly illustrate how the air quality in China improved over the past couple of months. The sudden drop in NO2 density was attributed to the decline of economic and industrial activities in the country due to the lockdown and travel restrictions.
As shown in the images, high concentrations of NO2 can be seen over certain parts of China from Jan. 1 to 20. However, after local authorities implemented travel bans to Wuhan, which is believed to be the source of the outbreak, NO2 density began to decrease. Within the last few weeks of February, concentrations of NO2 in China have almost disappeared.
According to NASA’s scientists, NO2 density over China is known to fluctuate due to international events. For instance, during the economic recession of 2008, NO2 concentrations dropped significantly. However, for Fei Lu, at air quality researcher at NASA, this year’s drop in NO2 levels is the biggest one yet.
“This year, the reduction rate is more significant than in past years and it has lasted longer,” she said in a statement. “I am not surprised because many cities nationwide have taken measures to minimize the spread of the virus.”
© Copyright IBTimes 2025. All rights reserved.




















