SpaceX’s Latest Mission For NASA Will Focus On Earth’s Oceans
KEY POINTS
- NASA awarded SpaceX with a new contract
- SpaceX will launch the PACE spacecraft using Falcon 9
- The mission will study phytoplankton in the oceans
NASA has awarded a new $80-million contract to SpaceX earlier this month. It focuses on a new mission that aims to study the ecosystems of Earth’s oceans.
The U.S. space agency finalized the contract with SpaceX on Feb. 4. It is valued at 80.4 million, which covers expenses related to the mission’s launch and other services.
As part of the agreement, SpaceX will launch NASA’s Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud ocean Ecosystem (PACE) spacecraft using its Falcon 9 rocket. The mission will officially kick-off with the launch of the rocket at Cape Canaveral in Florida sometime in December 2022. It will serve as the third science mission launched by SpaceX for NASA. The first two are the Jason-3 oceanography satellite and the TESS astronomy spacecraft.
PACE is a 1,700-kilogram spacecraft that’s designed to operate at an altitude of 676.5 kilometers. Once deployed, it will follow a Sun-synchronous orbit, which means the spacecraft will encircle Earth at the same rate as the planet goes around the Sun.
“SpaceX is honored to continue supporting NASA’s critical scientific observational missions by launching PACE, which will help humanity better understand, protect and preserve our planet,” Gwynne Shotwell, the COO of SpaceX said in a statement according to Space News.
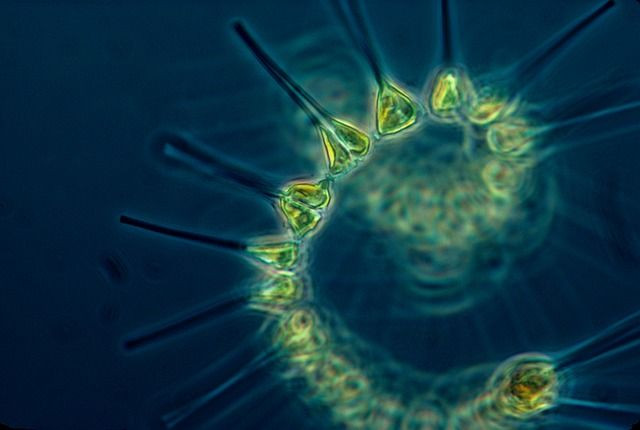
For its mission, the PACE spacecraft will be equipped with the Ocean Color Image. It will operate from ultraviolet to infrared shortwave to study phytoplankton in the ocean. Although phytoplankton are too small to be seen by the human eye, they can amass into massive patches on the surface of the water. Sometimes, these patches can be observed from low-Earth orbit.
Studying the development of phytoplankton is vital because these plant-like organisms serve as the main food source for numerous marine animals such as zooplankton and whales. Also, the process of photosynthesis by the phytoplankton accounts for up to half of the global primary production.
In addition to the phytoplankton in the oceans, NASA’s PACE spacecraft will also study the properties of clouds and aerosols in the sky.
“The PACE mission represents the nation’s next great investment in understanding and protecting our home planet,” NASA said in a statement.
© Copyright IBTimes 2025. All rights reserved.





















