US Mourns One Million Dead From Covid-19
The United States has crossed the threshold of one million deaths from Covid-19, the White House said on Thursday, as the nation seeks to turn the page on the pandemic despite threats of another surge.
"Today, we mark a tragic milestone," President Joe Biden said in a statement that acknowledged the "unrelenting" pain of bereaved families, and urged Americans to remain vigilant as cases tick back up.
"One million empty chairs around the dinner table," Biden said. "Each an irreplaceable loss. Each leaving behind a family, a community, and a nation forever changed."
Biden's announcement came as he chaired a global virtual Covid summit, taking place as Europe also passed two million Covid deaths, focused on efforts to bring the pandemic under control worldwide and prepare for future health emergencies.

The US leader came to the summit hobbled by Congress' failure to approve $22.5 billion in continued emergency Covid funding, including for the international supply of vaccines, and he warned it was "critical" for lawmakers to keep financing testing, vaccines and treatments.
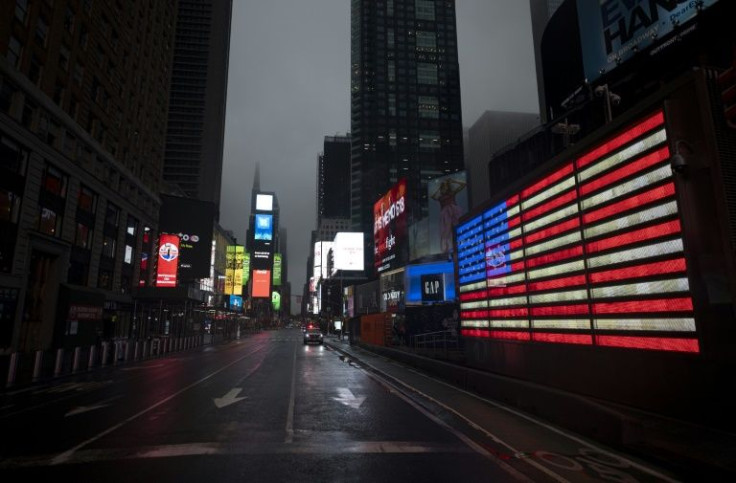
America recorded its first Covid-19 death, on the West Coast, in early February 2020. By the next month, the virus was ravaging New York and the White House was predicting up to 240,000 deaths nationwide.
But those projections were way off.
Even in New York -- the hard-hit early epicenter of America's Covid crisis -- the million death milestone was difficult to comprehend.
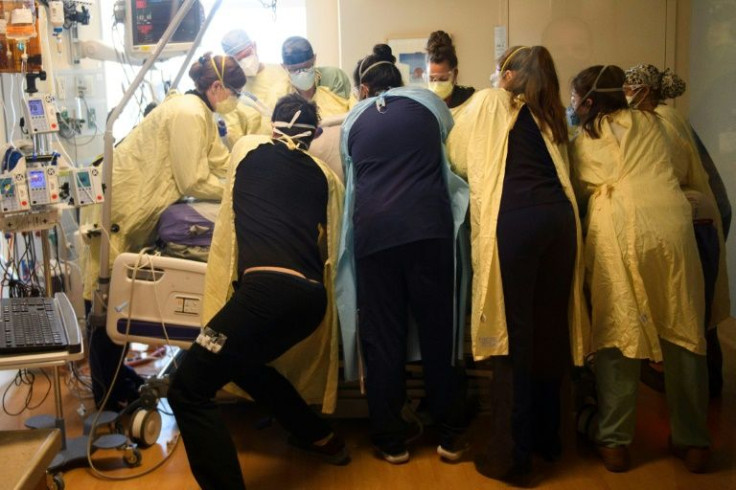
"It's unfathomable," Diana Berrent, one of the first people in New York state to catch Covid-19, said of the toll that far exceeds epidemiologists' worst predictions.
Back in spring 2020, New York City hospitals and morgues overflowed, and the sound of ambulance sirens rang down empty streets as then-president Donald Trump responded chaotically in Washington.
Two years on, and life in the Big Apple is largely back to normal as residents attempt to put the collective trauma of the virus that has killed 40,000 New Yorkers behind them.
Broadway stage lights are once again illuminated, yellow taxis clog main avenues and bars in business districts hum with post-work chatter.

"Without a doubt you feel the energy of the people that are on the streets. It's been a long time coming," Alfred Cerullo, president of a business improvement group in Midtown Manhattan, told AFP.
New York's rebound has been aided by its high inoculation numbers -- about 88 percent of adults are fully vaccinated, a rate that was boosted by mandates, including for indoor activities like dining.
Jeffrey Bank, owner of Carmine's restaurant near Times Square, says sales at the Italian eatery are better than they were in 2019, as residents and tourists make up for lost time.
"People have been sitting at home for two years. They want to celebrate and they're entitled to," he told AFP.
But the city has a long way to go. Many stores remain empty and only 38 percent of Manhattan workers are in the office on an average weekday, according to Kastle Systems, a security firm that tracks building occupancy.
The Big Apple's tourism board also doesn't expect visitor numbers to get back to the 67 million of 2019 people for a few years, and business owners fear another wave of infections.
In recent weeks, the United States has seen an uptick in the number of daily virus cases, largely due to the new Omicron subvariant.
The rise has coincided with the lifting of mask mandates.
"I think we are in a place where psychologically and socially and economically, people are largely done with the pandemic," said Celine Gounder, an infectious disease expert at New York University.
"(But) the pandemic is not over. So you have a disconnect between what is happening epidemiologically and what's happening in terms of how people are responding," she told AFP.
Among the most at-risk are the unvaccinated, lower-income populations, uninsured people and communities of color, she says.
Ideological clashes over curfews and mask and vaccine mandates characterized America's early pandemic response, as it racked up the world's highest death toll, with hospitals overwhelmed and morgues failing to keep up with the dead.
Trump was late to back social distancing, repeatedly undermined top scientist Anthony Fauci, peddled unproven medical treatments, and politicized mask-wearing -- before eventually being hospitalized with the virus himself.
Trump did pump billions of dollars into vaccine research and by mid-December 2020, the first vaccines were available for health care workers.
But deaths kept soaring amid a slow take-up of shots in conservative areas of the country.
New president Biden and many Democratic governors enforced mandates but Republican-led states like Florida and Texas outright banned them, highlighting America's patchwork of rules that made forming a unified response to the pandemic difficult.
© Copyright AFP {{Year}}. All rights reserved.





















