AI May Help Speed Up Drug Discovery, Fight Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria
KEY POINTS
- Researchers have discovered a compound that can kill antibiotic-resistant bacteria using AI
- Halicin kills bacteria by attacking their electrochemical structures
- The researchers are using the technique to develop more such compounds
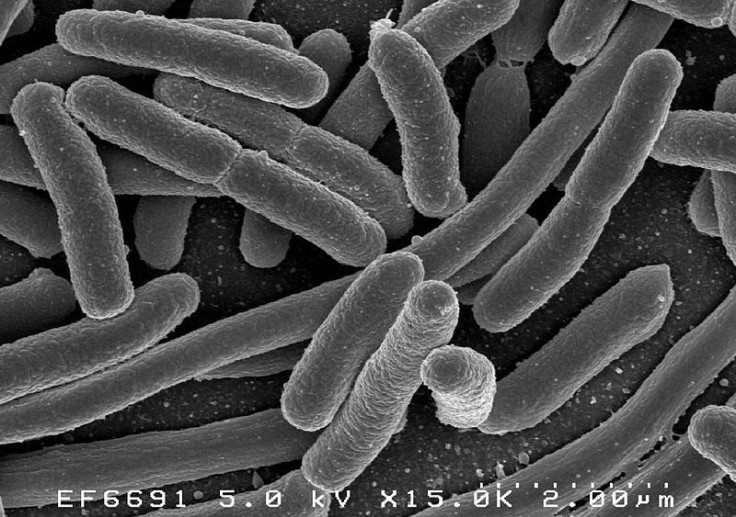
Artificial intelligence is providing a breakthrough in the medical field. Researchers at MIT have used AI to discover a compound, which will be able to kill even highly resistant bacteria efficiently.
The compound, Halicin, works differently than regular antibiotics. It kills bacteria by killing their ability to maintain the electrochemical gradient necessary to produce energy-storing molecules. Even bacteria such as E.Coli could not develop resistance for 30 days to Halicin, while it developed resistance to the conventional antibiotic ciprofloxacin within three days.
“We wanted to develop a platform that would allow us to harness the power of artificial intelligence to usher in a new age of antibiotic drug discovery. Our approach revealed this amazing molecule which is arguably one of the more powerful antibiotics that has been discovered,” James Collins, the Termeer Professor of Medical Engineering and Science in MIT’s Institute for Medical Engineering and Science (IMES) and Department of Biological Engineering stated in a press release.
The researchers have developed a system that finds molecular structures with bacteria-killing capabilities. The compounds found using this system are then studied using neural networks and mapped into continuous vectors, to predict their behavior. The researchers trained the AI to study the molecular structures of 1,700 established drugs and 800 natural products, along with 6,000 different compounds. Of all of these, the AI found Halicin to be the most effective.
However, one should wait before hailing Halicin as a wonder drug for fighting bacterial infections. While, in laboratory conditions, researchers were able to eradicate infections such as A.baumanii in mice, no human trials have been held for the molecule as yet. There is a long way to go before it can get an FDA certification. The researchers have stated in the press release that they are working to partner with pharmaceutical companies and not-for-profit institutions for facilitating human trials, although they haven't revealed a timeline for it yet.
The researchers are also trying to replicate the success they had with Halicin and are in the process of screening 100 million molecules for potential cures. They are also working on creating antibiotics from scratch and their side effects.
Halicin is a practical example of how AI is revolutionalizing the medical field. Drug discovery is a large, drawn-out process that takes years to complete. It takes researchers years to find the correct compound and study its effects.
Over time, many strains of bacteria develop resistance to treatments and make all existing treatments nearly ineffective. The fact that AI can help speed up drug discovery using not just permutations and combinations to find new compounds but also analyze their impact using neural networks, can significantly help speed up the process of bringing new drugs to the market to combat diseases. It cannot just save precious time, but can also help cut down on the massive costs incurred during drug development.
© Copyright IBTimes 2025. All rights reserved.




















